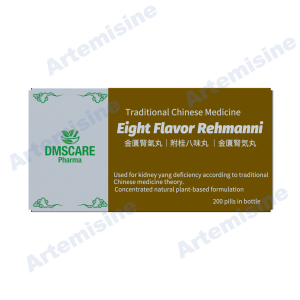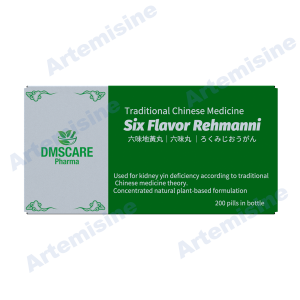

Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
Welcome to Sinophare
Important Knowledge

We sincerely hope that our efforts can help you have a peaceful experience of traditional Chinese medicine wisdom! 🌱 If you need specific prescription guidance, it is recommended to consult a local traditional Chinese medicine clinic or a certified physician certified by the World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies (WFCMS).